People with diabetes may be harbouring advanced vascular disease that could increase their risk of stroke, according to new research being presented next week at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). The findings suggest that arterial imaging with 3D MRI could be useful in helping to determine stroke risk among diabetics.
Narrowing of the carotid arteries is associated with risk of stroke, but less is known about stroke risk in people with little or no narrowing of these arteries. For the new study, researchers used 3D MRI to study the carotid arteries for evidence of intraplaque haemorrhage, an indicator of advanced atherosclerotic disease.
“A recent analysis of multiple studies has shown that people with carotid artery narrowing and intraplaque haemorrhage have a five- to six-times higher risk of stroke in the near future compared to people without,” said study author Tishan Maraj, imaging analyst at Sunnybrook Research Institute and MSc. candidate at the University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada.
Maraj and colleagues focused their study on people with diabetes, a group already facing a significantly increased risk of strokes with worse outcomes than the non-diabetic population. They used 3D MRI to investigate the prevalence of carotid intraplaque haemorrhage in 159 asymptomatic type 2 diabetic patients, average age 63, recruited from a dietary trial between 2010 and 2013.
Of the 159 patients imaged, 37, or 23.3%, had intraplaque haemorrhage in at least one carotid artery. Five of the 37 patients had intraplaque haemorrhage in both carotid arteries. Intraplaque haemorrhage was found in the absence of carotid artery stenosis, and was associated with an increased carotid artery wall volume as measured by 3D MRI.
“It was surprising that so many diabetic patients had this feature,” Maraj said. “We already knew that people with diabetes face three to five times the risk of stroke, so perhaps intraplaque haemorrhage is an early indicator of stroke risk that should be followed up.”
While 2D MRI has been used for more than a decade to identify and characterise carotid artery plaques, the 3D method brings an extra level of imaging power, Maraj noted.
“The advantage of 3D MRI is you can image the entire carotid artery and pinpoint the area of interest over a shorter period of time compared with multiple 2D sequences,” he said.
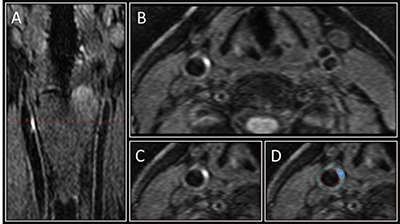
Figure 1: Image A shows the 3D MRI intraplaque haemorrhage sequence as acquired in the coronal plane. The red dotted line indicates the level at which the reformatted axial plane, B, was obtained. C shows the section of the right carotid artery with a region of high signal consistent with intraplaque haemorrhage. Contours are drawn for the outer wall (green) and lumen (red) with the area of intraplaque haemorrhage in this segment shaded blue in D.
Maraj emphasised that the study did not look at outcomes for the patients and did not draw any conclusions on whether people with intraplaque haemorrhage will develop carotid artery blockages more quickly than those with no intraplaque haemorrhage present. However, it is already known that blood is a destabilising factor of plaque that promotes rupture, setting off a chain of events that can lead to a stroke.
Although there is no treatment for intraplaque haemorrhage at this time, Maraj said identification of it may help with risk stratification and could even have applications in the non-diabetic population.
“Even though you cannot treat intraplaque haemorrhage, you can monitor patients a lot more closely,” he concluded.












